In order to use SDL Web 8.5 and ADFS, we first have to enable SSO (Single Sign-On) on the SDL Web side.
The setup I have is:
A prerequisite of enabling HTTPS is obtaining and installing a SSL Certificate. This is beyond the scope of this blog post, but the PowerShell script above expects the 40 character certificate thumbprint as a parameter.
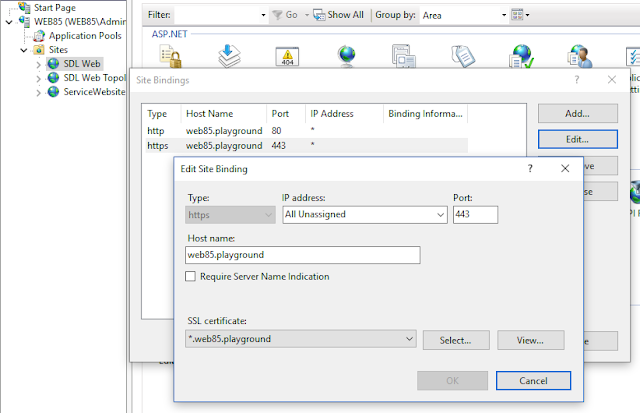
After running the PowerShell script, verify in IIS that the SDL CME website has a binding for port 443 (HTTPS) and that the SSL Certificate is configured for that binding.
The parameter UserNameHeader is an important one, because it defines the name of the request header that the HTTP Module SsoAgentHttpModule is reading in order to impersonate the CME user. This SsoAgentHttpModule is a module that comes out of the box with SDL Web and it is configured and enabled by the PowerShell script.
The authenticator performs the following tasks:
The ADFS SAML Authenticator is described in more detail in this blog post.
The setup I have is:
- SDL Web 8.5 installed in AWS (but it is the on-premise version of SDL Web)
- Active Directory outside of AWS
- ADFS outside of AWS, but somewhere close to AD
- HTTPS access to SDL Web CME website
For this setup to work, we need to enable/configure a few things:
- enable HTTPS access to the CME
- enable/configure SSO on the CME
- ADFS SAML Authenticator
Enable HTTPS
In PowerShell, run the script SetupHTTPS.ps1 from folder [SDLWebHome]\bin\Configuration Scripts. A very detailed explanation of this process is available at https://docs.sdl.com/LiveContent/content/en-US/SDL%20Web-v5/GUID-D694CEFB-AE01-415E-B919-5867C08E0A18.A prerequisite of enabling HTTPS is obtaining and installing a SSL Certificate. This is beyond the scope of this blog post, but the PowerShell script above expects the 40 character certificate thumbprint as a parameter.
After running the PowerShell script, verify in IIS that the SDL CME website has a binding for port 443 (HTTPS) and that the SSL Certificate is configured for that binding.

Enable SSO
In PowerShell, run the script SetupSSO.ps1 from folder [SDLWebHome]\bin\Configuration Scripts. A very detailed explanation of this process is available at https://docs.sdl.com/LiveContent/content/en-US/SDL%20Web-v1/GUID-32378192-5366-4805-85AF-C578F988993B.The parameter UserNameHeader is an important one, because it defines the name of the request header that the HTTP Module SsoAgentHttpModule is reading in order to impersonate the CME user. This SsoAgentHttpModule is a module that comes out of the box with SDL Web and it is configured and enabled by the PowerShell script.
ADFS SAML Authenticator
This is a custom piece of software that bridges the ADFS server with the SDL SsoAgentHttpModule.The authenticator performs the following tasks:
- request a SAML token to the ADFS server
- intercept POST back with SAML token from ADFS server
- decrypt token
- extract user name from token
- put user name in a request header
The ADFS SAML Authenticator is described in more detail in this blog post.

Comments